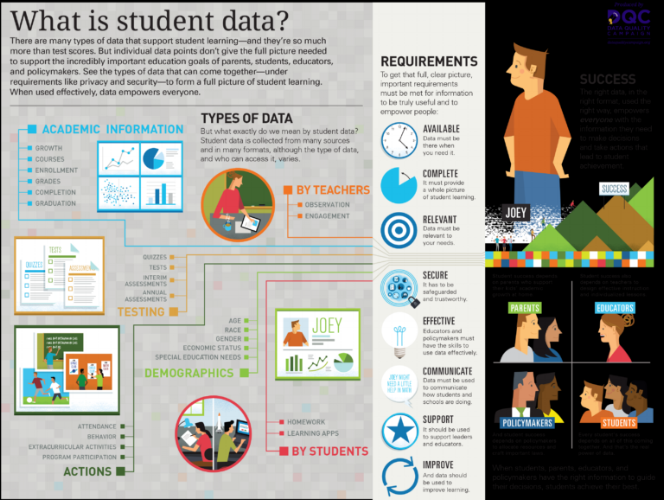
Student data defined per Education Reform glossary:
"In education, student-level data refers to any information that educators, schools, districts, and state agencies collect on individual students, including data such as personal information (e.g., a student’s age, gender, race, place of residence), enrollment information (e.g., the school a student attends, a student’s current grade level and years of attendance, the number of days a student was absent), academic information (e.g., the courses a student completed, the test scores and grades a students earned, the academic requirements a student has fulfilled), and various other forms of data collected and used by educators and educational institutions (e.g., information related to disciplinary problems, learning disabilities, medical and health issues, etc.)."
Data Literacy Defined:
Educators can use multiple sources of data, habits of mind, data properties, transformations of data, data management, data transformation, and communication to understand and analyze student data. Data literacy requires educators to include all student data, not just assessment, in their analysis and to realize that data collections is a continuous process (McMillan, 2018).